Insee Analyses ·
July 2022 · n° 74
Insee Analyses ·
July 2022 · n° 74 One third of the European Union's carbon footprint is due to its imports
One third of the European Union's carbon footprint is due to its imports
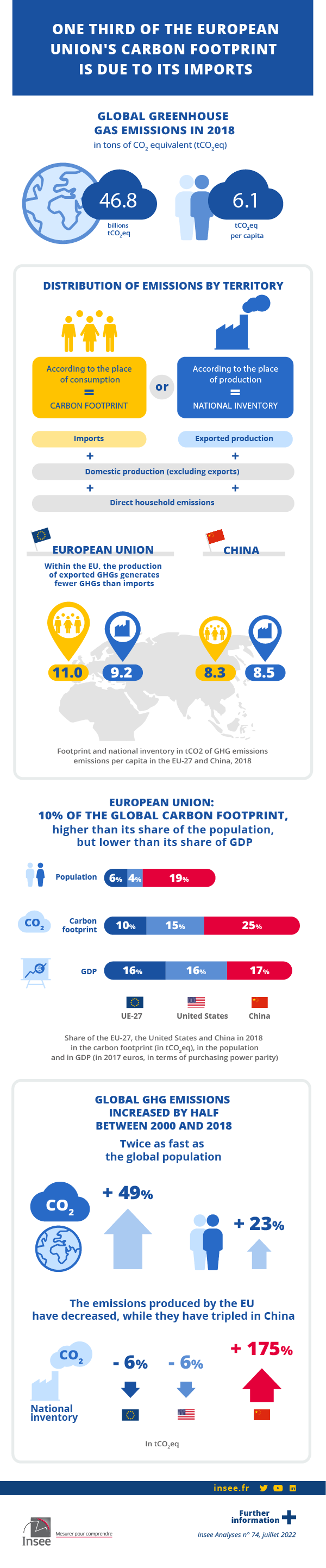
The European Union (EU) emits 1.5 times more greenhouse gases (GHG) per capita than the world average; the United States almost three times more. However, relative to their GDP, their GHG emissions are lower than the world average. The EU in particular emits less GHG to produce one euro of goods and services than any other geographical area. Within the EU, France's energy mix and, by extension, its overall production are less carbon intensive than that of its partners, notably Germany.
In the EU and the US, GHG emissions from final demand - the carbon footprint - are higher than emissions from production. Compared to theemissions inventory associated with production on a territory, the carbon footprint subtracts the emissions embodied in exported products but adds those embodied in imported products. In 2018, the EU's carbon footprint per capita was 11 tonnes of CO2 equivalent, compared to 21 in the US and 8 in China. About one third of the EU's footprint was due to production processlocated outside the EU.
Between 2000 and 2018, global GHG emissions increased by half when the population grew by a quarter. Emissions from the EU have decreased, but in China they have tripled during the same period of time.